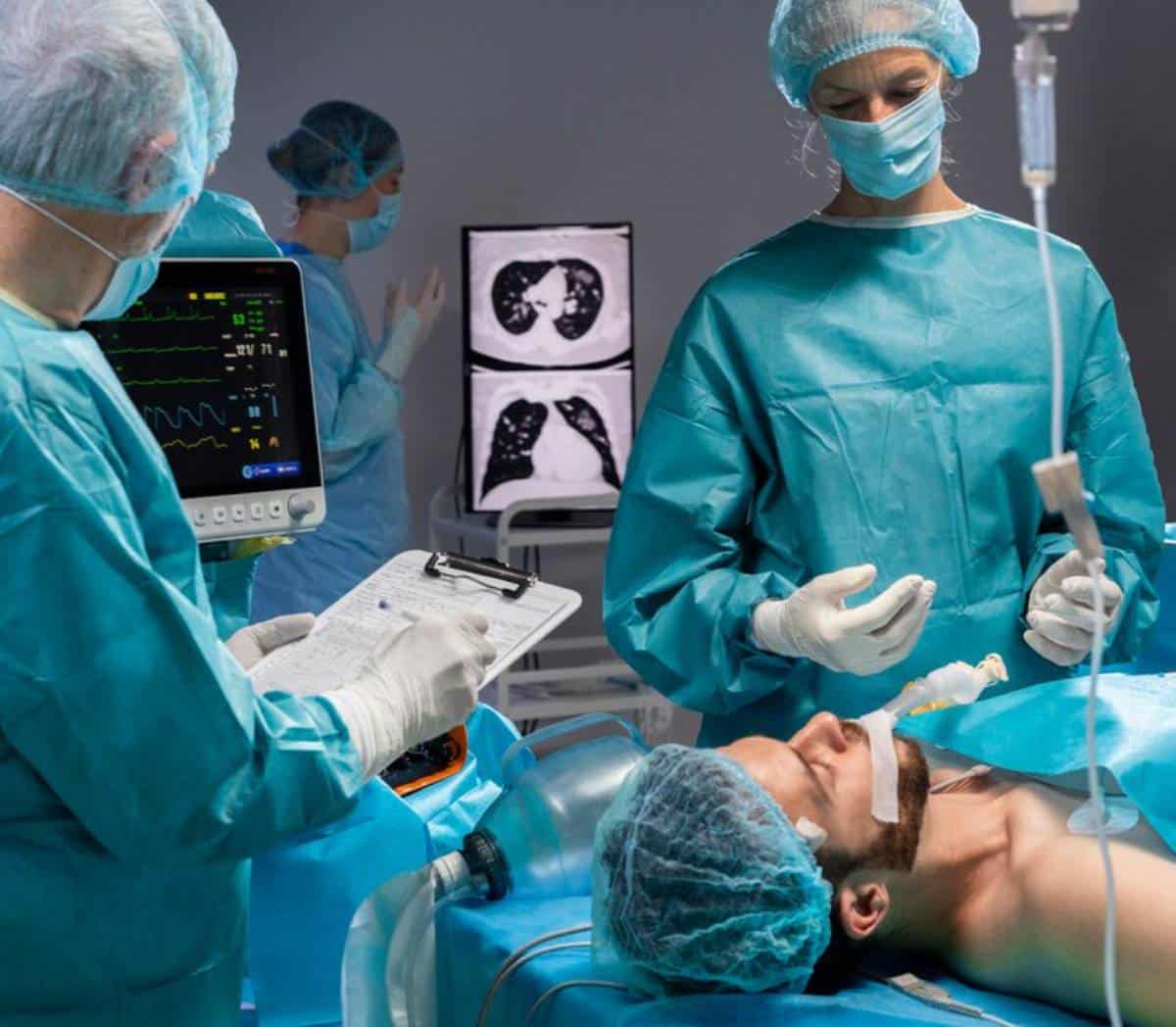
Robotic Surgery Advancements Transforming Healthcare
The operating theatre is evolving. Gone are the days when surgical instruments were limited to a surgeon’s steady hand alone. Today, advanced technology is transforming surgery. It guides scalpel and stitch, changing how procedures are done. Robotic surgery leads this change. It’s a fast-growing field that merges engineering precision with medical skills.
Robotic surgical systems, driven by medical robotics and healthcare AI, are changing modern medicine. From minimally invasive techniques to improved recovery times and reduced complications, robotic-assisted procedures are enhancing outcomes for both patients and clinicians.
This article looks at how robotic surgery is changing healthcare. It impacts everything from the operating room to the recovery ward. We’ll also discuss what the future might bring for this exciting blend of robotics and medicine.
What Is Robotic Surgery?
Robotic surgery involves the use of robotic systems to aid in surgical procedures. These systems aren’t autonomous. Trained surgeons control them using robotic arms to make precise movements, often through small incisions.
The da Vinci Surgical System is the most famous one. Surgeons can use a console with hand and foot controls to operate robotic tools. Advanced cameras give clear, 3D views of the surgical site. This helps improve precision and lowers the chance of mistakes.
Key Components of Medical Robotics in Surgery
1. Robotic Arms
These are the main tools used in surgery. They can mimic the fine motor skills of human hands, but they offer better stability and flexibility.
2. Surgeon Console
A workstation lets the surgeon see a 3D image and control the robotic arms with joystick-like tools.
3. Vision System
High-resolution imaging tools give a clear view of the operative field. They work well, even in hard-to-reach areas that regular tools can’t access.
4. AI Integration
Emerging systems are increasingly incorporating healthcare AI for:
- Real-time decision support
- Image recognition and diagnostics
- Robotic learning from large datasets of previous surgeries
Benefits of Robotic Surgery
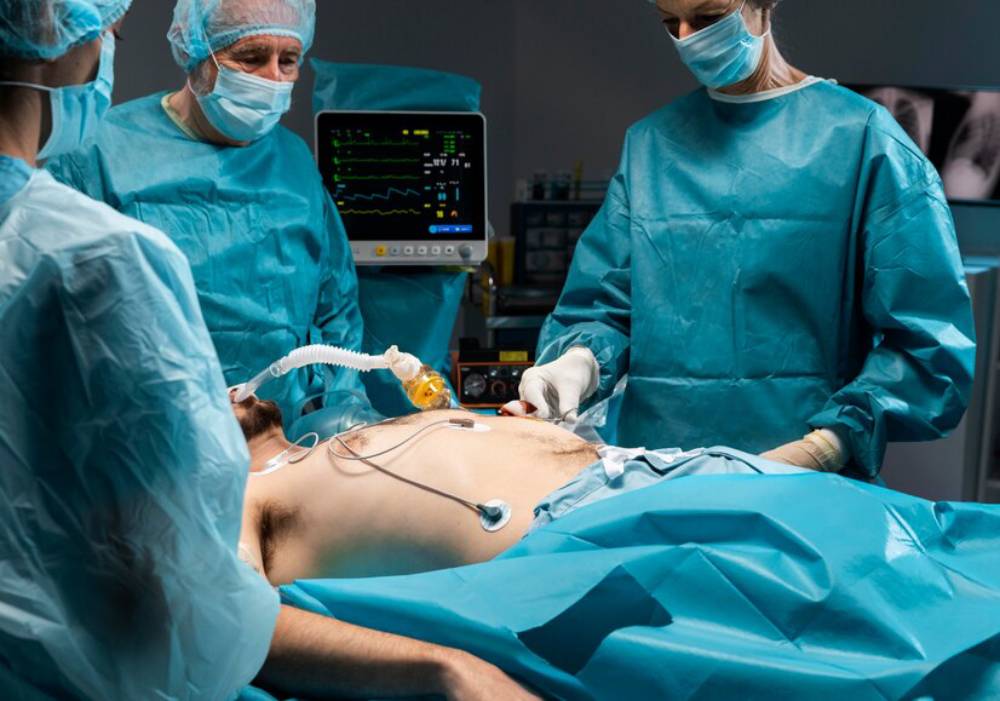
The integration of robotics and AI is not simply a matter of technological novelty. It offers tangible advantages that are transforming patient care.
1. Minimally Invasive Techniques
Robotic tools allow for smaller incisions, which means:
- Less blood loss
- Reduced risk of infection
- Shorter hospital stays
- Faster recovery
2. Enhanced Precision
Surgeons perform delicate procedures with precision, particularly in neurosurgery, cardiac surgery, and urology.
3. Improved Visualisation
High-definition 3D imaging offers clearer views than the human eye. This helps with safer navigation around delicate structures.
4. Reduced Surgeon Fatigue
Ergonomic controls and support systems lower physical strain on surgeons during long procedures. This leads to better performance and outcomes.
Robotic Surgery in Practice: Current Applications
1. General Surgery
Robotic systems are increasingly used in gallbladder removals, hernia repairs, and colon resections. Smaller incisions mean better cosmetic results and quicker returns to normal life.
2. Gynaecological Surgery
Medical robotics improve procedures like hysterectomies and endometriosis treatment. They offer better precision and easier access.
3. Urology
Prostatectomies are among the most common robotic surgeries. Robotics helps surgeons protect nerve bundles and other important structures needed for function.
4. Cardiac Surgery
Robotic-assisted procedures in heart care offer less invasive options for valve repair and coronary artery bypass. This approach reduces trauma to the chest wall.
5. Orthopaedics
MAKOplasty systems use AI and robotics for joint replacements. This helps surgeons customise procedures to fit each patient’s unique anatomy.
The Role of Healthcare AI in Robotic Surgery

Artificial Intelligence is amplifying the capabilities of medical robotics in several ways:
1. Pre-operative Planning
AI can analyse medical images and patient data. It helps surgeons plan the best surgical approach.
2. Intraoperative Assistance
During surgery, AI-powered systems can:
- Alert surgeons to potential risks
- Suggest real-time adjustments
- Monitor instrument positions
3. Post-operative Monitoring
AI tools help track patient recovery, identify complications early, and personalise rehabilitation plans.
Healthcare AI is making surgery more data-driven and adaptive. This helps reduce variation and improve outcomes for different patient groups.
Leading Technologies and Innovators
1. da Vinci Surgical System (Intuitive Surgical)
The top name in robotic-assisted surgery, popular in urology, gynaecology, and general surgery.
2. MAKO (Stryker)
MAKO focuses on orthopaedic procedures. It combines pre-surgical planning with robotic precision for hip and knee replacements.
3. Versius (CMR Surgical)
A new competitor is focusing on modular and flexible robotics. These robots can be used for various minimally invasive procedures.
4. Hugo (Medtronic)
It blends robotics with AI insights and global connectivity. The goal is to introduce robotic surgery to emerging markets.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its promise, robotic surgery faces several obstacles:
1. High Costs
Systems can cost millions to buy and keep running. This high cost limits access, especially in low-resource areas.
2. Training Requirements
Surgeons need a lot of training to use robotic systems safely. This can slow down how quickly they are adopted.
3. Lack of Tactile Feedback
Current robotic systems still can’t match the “feel” of traditional surgery. This touch is crucial for some procedures.
4. System Failures
Like all technology, robotic systems can have software glitches or mechanical faults. So, they need backup protocols.
The Future of Robotic Surgery
1. Smaller, More Affordable Robots
Innovators are creating compact systems for smaller hospitals and outpatient clinics. This aims to make robotic care available to more people.
2. Tactile Sensory Feedback
Work is in progress to add haptic feedback. This will let surgeons “feel” pressure, resistance, and texture.
3. Autonomous and Semi-Autonomous Robots
Right now, surgeons do most tasks, but future systems may take on some routine jobs by themselves. They could assist with repetitive or very precise steps.
4. Tele-surgery
New tech in connectivity and robotics could let specialists do surgery from afar. This means they can share their skills with remote or underserved areas right away.
5. AI-enhanced Decision Making
With continuous learning from global databases of surgical outcomes, AI will assist in:
- Customising procedures
- Preventing complications
- Optimising surgical techniques
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
As healthcare AI becomes more embedded in surgical decision-making, ethical oversight is essential.
Key Questions:
- Who is accountable for AI-assisted decisions in surgery?
- How can we ensure informed consent when AI is involved?
- What data privacy protections are in place for surgical planning tools?
Regulators must update medical standards and certification rules. This is needed to keep up with the changing role of robotics and AI in healthcare.
A Revolution in the Operating Room
Robotic surgery is not just the future; it’s here now. It’s changing how medicine is done all over the world. Thanks to medical robotics and healthcare AI, surgeons can work more precisely. Patients recover faster, and hospitals use resources more efficiently.
Challenges like cost, training, and regulation still exist. Robotic-assisted surgery will soon become standard practice, not just a speciality. As technology evolves, we get closer to a healthcare system. Here, intelligent machines help skilled humans improve precision, safety, and patient outcomes.
Act now! No matter if you’re a medical pro, a tech fan, or a future patient, keep up with the fast-changing world of robotic healthcare. Because the next time you’re in an operating room, a robot might be part of the team saving your life.


